Polyethylene is the most widely used plastic in the polyolefin family. Polyethylene is a widely used plastic that is often used in the production of common plastic products such as bottles, pots, gallons, tankers, bags, toys, pipes, etc.
Polyethylene is one of the most popular plastics. Along with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polypropylene (PP) it is what we call high-end industrial plastics: plastic that is produced in large volumes and is available at an affordable cost.

Polyethylene has a wide range of applications. Used for plastic containers, bottles, bags, plastic toys, films, pipes, plastic parts, laminates, etc.
Basically, if you want to use plastic products in a field that does not require special properties, PE can be an ideal choice. Under certain conditions, polyethylene can compete with engineered plastics. As you can imagine, due to its low cost and wide availability, polyethylene has been widely used in various industrial and manufacturing sectors.
Also, keep in mind that we often talk about polyethylene, but in fact, this lightweight and durable thermoplastic comes in different crystal structures that make all the difference in the selection process and final properties!
We will help you find the product you want from the many options available. Today, there are more than 6 thousand grades by more than 250 manufacturers in the market.
Comparison of polyethylene and polypropylene
Both polyethylene and polypropylene are polyolefins. Today, these two thermoplastics are the most widely used polymers, but when it comes to selection, they differ in many aspects such as chemical resistance, flexibility and density, temperature resistance, etc. Deciding which polyolefin to choose depends solely on your intended use.
Polyethylene is mostly used for films and sheets in packaging due to its excellent flexibility. On the other hand, PP is stiffer than polyethylene. While both polymers have excellent chemical resistance, PE (especially HDPE) behaves exceptionally well under the same exposure conditions. Both PP and PE have poor performance against UV rays and require proper resistance.

Comparing PE and PET – which one is right for your packaging?
PE and PET are both popular when it comes to packaging. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is an unbreakable and lightweight material that is used for packaging food and health products due to its non-reactive properties. One of the drawbacks of PET is that it is only temperature resistant up to 80°C. On the other hand, polyethylene, especially HDPE, can withstand a temperature range of 126 to 131°C and offers a higher operating temperature. When it comes to HDPE vs. PET, polyethylene can be the ideal choice for those looking for a plastic that can withstand a variety of factors while maintaining its strength – both rigid and flexible. acceptable

PE, PU and PVC – which one is suitable for making pipes?
Polyethylene, polyurethane and PVC are widely used thermoplastics for agricultural pipes, hose pipes and for the production of various types of custom pipes. Although no plastic pipe can have all the features we want because there are certain differences that you should consider in each application field.
Compared to PU, polyethylene is less flexible but has good moisture resistance. Polyurethane tubing is used where flexibility, kink resistance along with high abrasion resistance is required, such as cable sheathing, pneumatic controls, analytical instrumentation, industrial, marine, mining, landfill, pipeline applications. Agriculture and…
On the other hand, flexible PVC has several advantages such as high chemical and corrosion resistance, excellent wear resistance and outstanding rubber-like flexibility. These features enable the use of PVC pipe in general industrial, food and beverage, potable water lines, medical, chemical, fuel, oil and mechanical applications.
Now if you know that polyethylene is the right material for you, we will help you to understand which type of polyethylene is best for you. Let’s start with some basics.

What is polyethylene and how is it made?
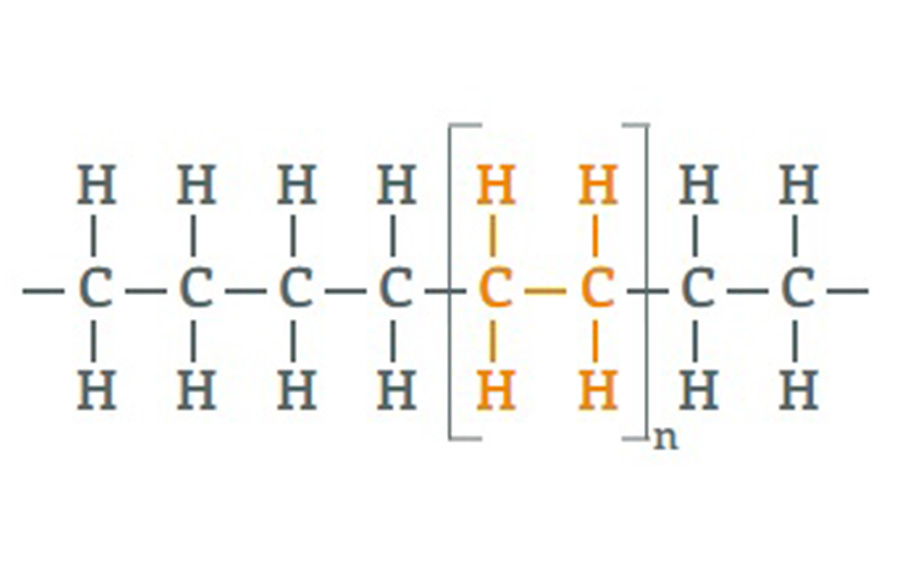
PE is a polyolefin made from the polymerization of ethylene (or ethene) monomer. The chemical formula of polyethylene is (C2H4)n.
Polyethylene chains are produced by addition or radical polymerization. Both Ziegler-Natta and metallocene catalysts are possible synthesis methods.
Common types of polyethylene (PE)
Depending on its density and branching, different grades of polyethylene can perform very differently from each other.
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
Medium Density Polyethylene (MDPE)
Ultra low density polyethylene (ULDPE)
High molecular weight polyethylene (HMWPE)
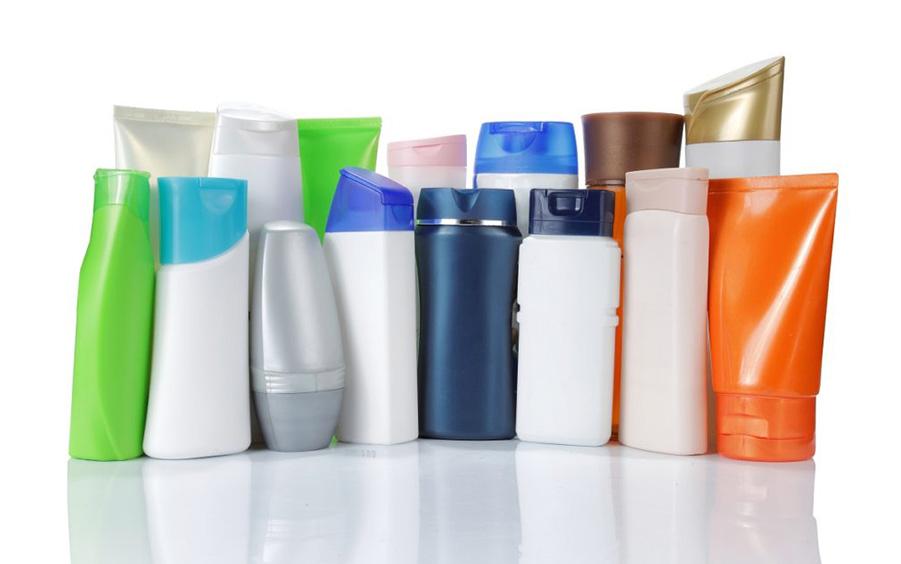

High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is a cost-effective thermoplastic with a linear structure and no or low degree of branching. It is produced at low temperature (70-300°C) and pressure (10-80 bar) and is obtained from reformed natural gas (mixture of methane, ethane, propane) or catalytic cracking of crude oil into gasoline.
HDPE is mainly produced using two methods: slurry polymerization or gas phase polymerization.
High-density polyethylene is flexible, semi-transparent, waxy, weather-resistant, and exhibits toughness at very low temperatures.

Properties of high density polyethylene products
HDPE melting point: 120-140 degrees Celsius
Density of HDPE: 0.93-0.97, g/cm3
Chemical resistance of high density polyethylene:
Excellent resistance to most solvents
Very good resistance to alcohols, dilute acids and alkalis
Moderate resistance to oil and grease
Poor resistance to hydrocarbons (aliphatic, aromatic, halogenated)
Continuous temperature: -50°C to +60°C, relatively rigid material with useful temperature capability
Higher tensile strength compared to other types of polyethylene
Low cost polymer with good processability
Good low temperature resistance
Excellent electrical insulation properties
Very little water absorption
Disadvantages of HDPE
Prone to cracking under stress
Less stiffness than polypropylene
High mold shrinkage
Poor resistance to ultraviolet rays and low heat
High frequency welding and joining is impossible
However, some variants are intelligently upgraded and some profiles offer improved performance.
Applications of high density polyethylene (HDPE)
The excellent combination of properties makes HDPE an ideal material in various industrial applications. Some of the major applications of high density polyethylene are:
Packaging applications – high density polyethylene is used in several packaging applications including boxes, trays, milk and fruit juice bottles, lids for food packaging, production of cans, drums, industrial bulk containers, etc. to be
Consumer Goods – Low cost and easy processability make HDPE the material of choice in several household/consumer goods such as trash cans, housewares, ice boxes, toys, etc.
Fibers and Textiles – Due to its high tensile strength, HDPE is widely used for agricultural applications such as ropes, fishing and sports nets, nets, as well as industrial and decorative fabrics.
Other uses of HDPE include pipes and fittings (gas pipes, water, sewage, drainage, sea outlet, industrial uses, cable protection, steel pipe covering, large inspection rooms, etc.) due to its excellent resistance to chemicals. and hydrolysis, automobile – fuel tanks, wiring and cable – energy sheet, telecommunication cables.
In general, HDPE is stiffer compared to other polyethylenes due to its high crystallinity (over 90%), but this means it is less transparent.
low density polyethylene (LDPE)
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a semi-hard polymer with low crystallinity (50-60%). Compared to HDPE, it has a higher degree of short and long side chain branching. LDPE consists of 4,000 to 40,000 carbon atoms with many short branches. It is produced at high pressure (1000-3000 bar; 300-80°C) through free radical polymerization process.

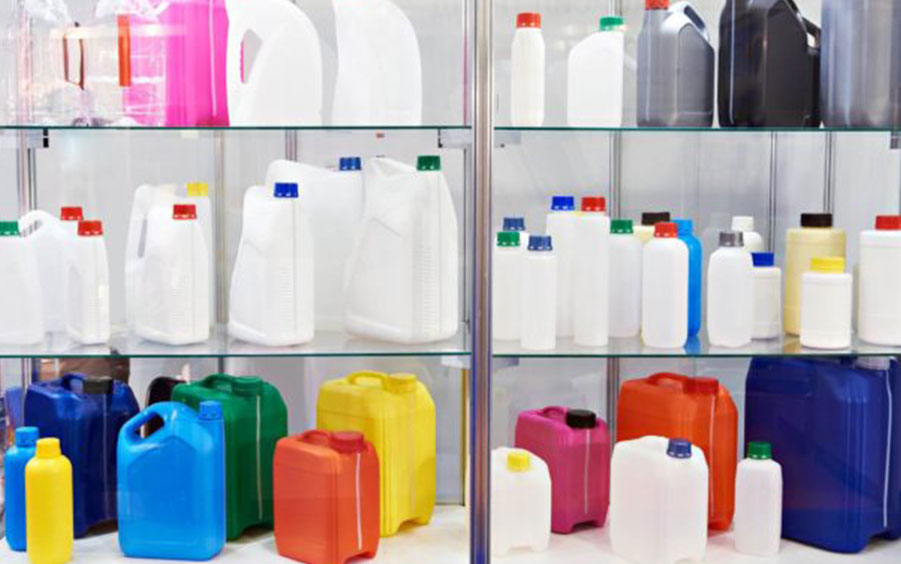
Properties of low density polyethylene products
Melting point 105-115 degrees Celsius
Density of LDPE: 0.910-0.940 g/cm3
LDPE chemical resistance: It has good resistance to alcohols, dilute alkalis and acids
Limited resistance to aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, mineral oils, oxidizing agents and halogenated hydrocarbons.
Temperature resistance up to 80°C continuously and 95°C for shorter times.
Low cost polymer with good processability
High impact strength at low temperature
Excellent electrical insulation properties
Very little water absorption
Transparent in the form of a thin layer
Disadvantages of low density polyethylene LDPE
The presence of more branching in the polymer chain brings certain problems for the performance of LDPE. As:
Prone to cracking under stress
Low strength, high temperature stiffness. This limits its use in places that require extreme temperatures.
High gas permeability, especially carbon dioxide
Poor resistance to ultraviolet rays
Highly flammable
High frequency welding and joining is impossible
To overcome these challenges, several LDPE grades have been developed with improved properties such as UV stabilization, high strength, anti-clogging, etc.
Applications of low density polyethylene (LDPE)
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) applications mainly revolve around manufacturing containers, sanitary bottles, wash bottles, pipes, plastic bags, computer parts, and various laboratory equipment. The most popular application of low density polyethylene is plastic bags.
Packaging – Due to its low cost and good flexibility, LDPE is used in the packaging industry for pharmaceutical bottles and lids, liners, garbage bags, food packaging bags (frozen, dry goods, etc.), laminates will be
Pipes and fittings – low density polyethylene is used for the production of pipes and water hoses for the pipe and fittings industry due to its flexibility and low water absorption.
Other applications include consumer goods – home appliances, flexible toys, wiring and cables – sub-conductor insulators, cable sheathing.
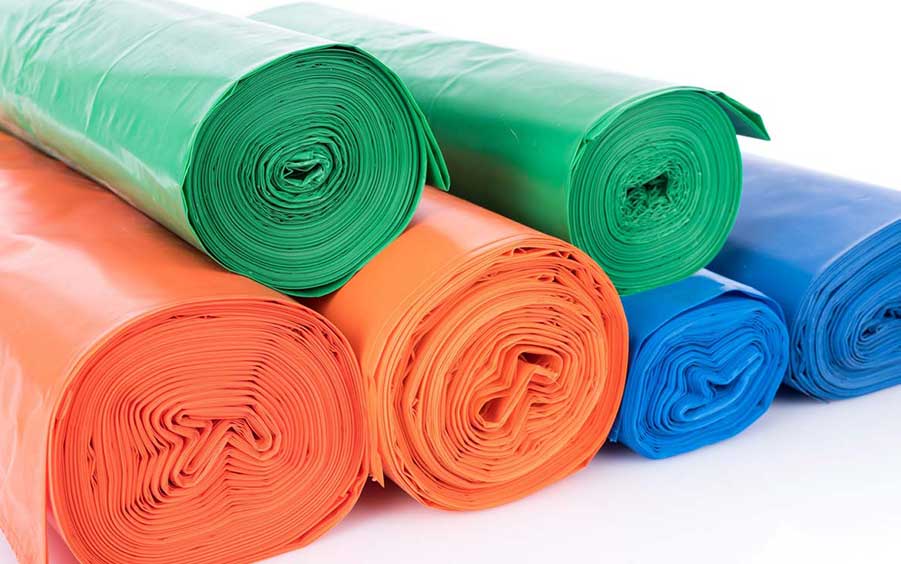

Recycling of polyethylene products
LDPE and HDPE are non-biodegradable in nature and contribute significantly to the production of plastic waste in the world. Both forms of polyethylene are recyclable and are used to produce bottles for non-food items, plastics for outdoor applications, compost bins, and more.
In solid form, polyethylene is inherently safe and non-toxic, but can be toxic if inhaled and/or absorbed as a vapor or liquid (ie, during manufacturing processes).

Production of bottles and polyethylene products
Plastic injection machines and blow molding machines are used to produce all kinds of plastic products.
Pars Polymer produces all kinds of bottles and polyethylene plastic products using the most up-to-date and advanced machines in the world. The use of advanced devices produces high-quality products at an affordable price, which makes us different from other manufacturers.
You can contact our experts for technical advice and guidance regarding the purchase of various polymer products.

I’ve had positive experiences negotiating prices with sellers through the messaging system.
The ability to save favorite searches for future reference is a convenient tool.